Key Generation Using Aes Algorithm
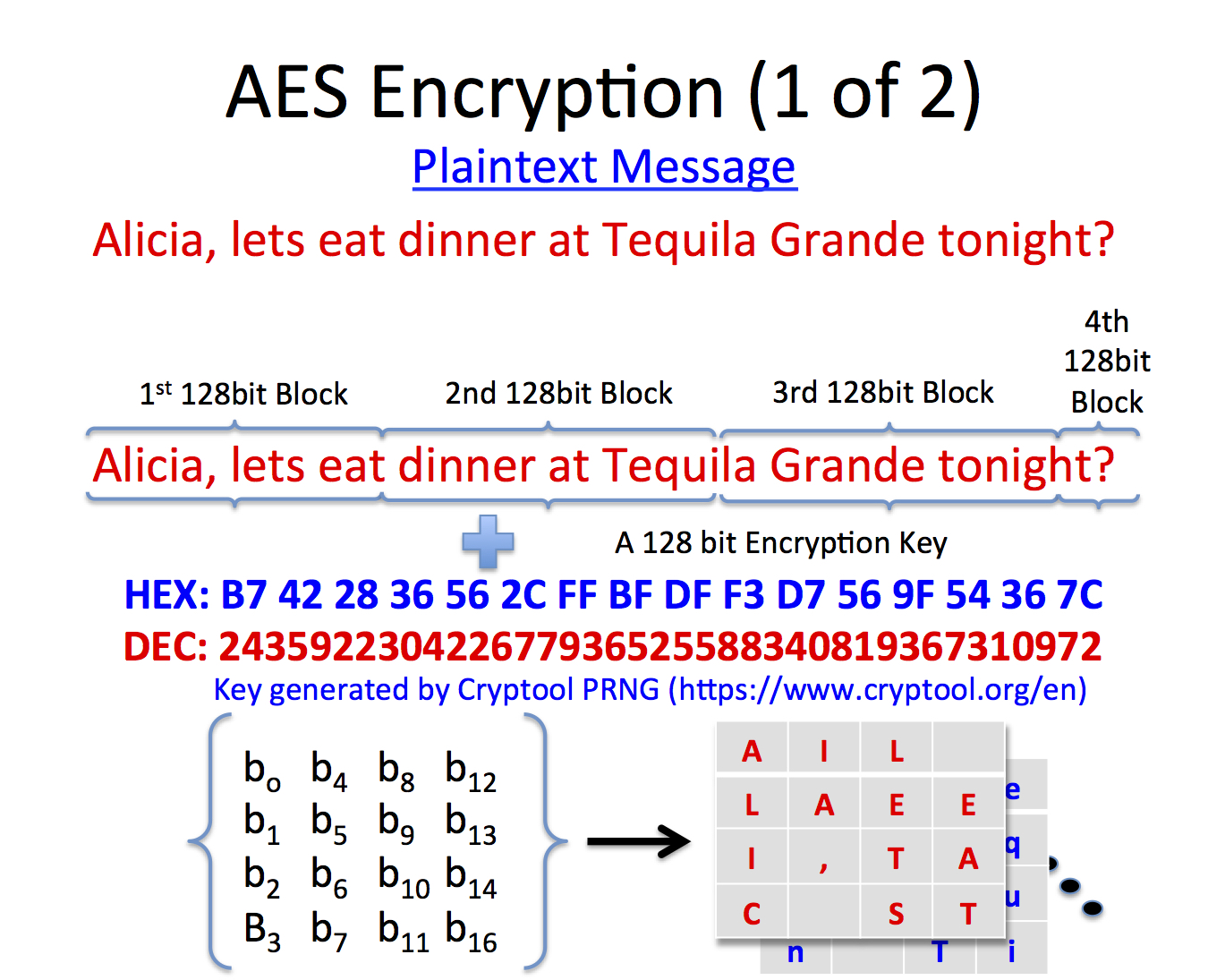
Posted By admin On 16.12.20The AES algorithm is most widely used algorithm for various security based applications. Security of the AES algorithm can be increased by using biometric for generating a key. The AES encryption algorithm encrypts and decrypts data in blocks of 128 bits. It can do this using 128-bit, 192-bit, or 256-bit keys. AES using 128-bit keys is often referred to as AES-128, and so on. The following diagram provides a simplified overview of the AES process Plain text. This is the sensitive data that you wish to encrypt.
Key generation is the process of generating keys for cryptography. The key is used to encrypt and decrypt data whatever the data is being encrypted or decrypted.
Modern cryptographic systems include symmetric-key algorithms (such as DES and AES) and public-key algorithms (such as RSA). Symmetric-key algorithms use a single shared key; keeping data secret requires keeping this key secret. Public-key algorithms use a public key and a private key. The public key is made available to anyone (often by means of a digital certificate). A sender will encrypt data with the public key; only the holder of the private key can decrypt this data.
Since public-key algorithms tend to be much slower than symmetric-key algorithms, modern systems such as TLS and its predecessor SSL as well as the SSH use a combination of the two in which:
- One party receives the other's public key, and encrypts a small piece of data (either a symmetric key or some data that will be used to generate it).
- The remainder of the conversation (the remaining party) uses a (typically faster) symmetric-key algorithm for encryption.
The simplest method to read encrypted data is a brute force attack–simply attempting every number, up to the maximum length of the key. Therefore, it is important to use a sufficiently long key length; longer keys take exponentially longer time to attack, making a brute force attack invisible and impractical.
Currently, commonly used key lengths are:
- 128-bits for symmetric key algorithms.
- 1024-bits for public-key algorithms.
Key generation algorithms[changechange source]
In computer cryptography keys are integers. In some cases keys are randomly generated using a random number generator (RNG) or pseudorandom number generator (PRNG), the latter being a computeralgorithm that produces data which appears random under analysis. Some types the PRNGs algorithms utilize system entropy to generate a seed data, such seeds produce better results, since this makes the initial conditions of the PRNG much more difficult for an attacker to guess.
In other situations, the key is created using a passphrase and a key generation algorithm, using a cryptographic hash function such as SHA-1.
Related pages[changechange source]
- Distributed key generation: For some protocols no party should be in the sole possession of the secret key. Rather, during distributed key generation every party obtains a share of the key. A threshold of the participating parties need to work together in order to achieve a cryptographic task, such as decrypting a message.
References[changechange source]
The Java KeyGenerator class (javax.crypto.KeyGenerator) is used to generate symmetric encryption keys. A symmetric encryption key is a key that is used for both encryption and decryption of data, by a symmetric encryption algorithm. In this Java KeyGenerator tutorial I will show you how to generate symmetric encryption keys.
Creating a KeyGenerator Instance
Before you can use the Java KeyGenerator class you must create a KeyGenerator instance. You create a KeyGenerator instance by calling the static method getInstance() passing as parameter the name of the encryption algorithm to create a key for. Here is an example of creating a Java KeyGenerator instance:
This example creates a KeyGenerator instance which can generate keys for the AES encryption algorithm.
Initializing the KeyGenerator
After creating the KeyGenerator instance you must initialize it. Initializing a KeyGenerator instance is done by calling its init() method. Here is an example of initializing a KeyGenerator instance:
The KeyGeneratorinit() method takes two parameters: The bit size of the keys to generate, and a SecureRandom that is used during key generation. Generate aes key and iv java.
Generating a Key
Once the Java KeyGenerator instance is initialized you can use it to generate keys. Generating a key is done by calling the KeyGeneratorgenerateKey() method. Avatar the game keygen activation key generator. Here is an example of generating a symmetric key: