C# Generate Random Encryption Key
Posted By admin On 17.12.20
- C Programming Tutorial
- C Programming useful Resources
- Oct 04, 2010 The idea is to create a completely random key, encrypt the desired data with it, and then somehow share the key with the consumer so that they can decrypt the data, passing both the key and the data to the consumer.
- Generate ASP.NET Machine Keys This tool allows you to create a valid random machine key for validation and encryption/decryption of ASP.NET view state. This is beneficial in a webfarm where all of the server nodes need to have the same machine key, and it is also beneficial on a single box to keep the machine key consistent between IIS recycles.
- About RandomKeygen Our free mobile-friendly tool offers a variety of randomly generated keys and passwords you can use to secure any application, service or device. Simply click to copy a password or press the ' Generate ' button for an entirely new set.
- (C#) Generate Encryption Key Discusses symmetric encryption key generation techniques for block encryption algorithms such as AES, Blowfish, and Twofish, or for other algorithms such as ChaCha20. Chilkat.NET Downloads.
- Selected Reading
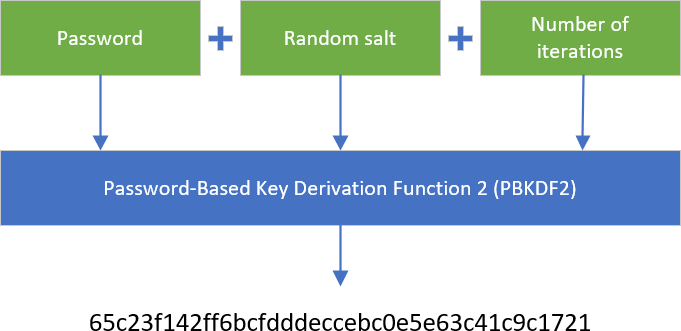
C# AES Encryption random IV per file. Ask Question Asked 3 years, 4 months ago. Generating the saltBytes based on the password is a bad idea. The salt should be random and if two users with the exact same password have the same salt, well now either of them can attack the other. C# AES Encryption. Encrypt and decrypt a message using.
An operator is a symbol that tells the compiler to perform specific mathematical or logical functions. C language is rich in built-in operators and provides the following types of operators −
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Misc Operators
We will, in this chapter, look into the way each operator works.
Arithmetic Operators
The following table shows all the arithmetic operators supported by the C language. Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 20 then −
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Adds two operands. | A + B = 30 |
| − | Subtracts second operand from the first. | A − B = -10 |
| * | Multiplies both operands. | A * B = 200 |
| / | Divides numerator by de-numerator. | B / A = 2 |
| % | Modulus Operator and remainder of after an integer division. | B % A = 0 |
| ++ | Increment operator increases the integer value by one. | A++ = 11 |
| -- | Decrement operator decreases the integer value by one. | A-- = 9 |
Relational Operators
The following table shows all the relational operators supported by C. Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 20 then −
C'est La Vie
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Checks if the values of two operands are equal or not. If yes, then the condition becomes true. | (A B) is not true. | |
| != | Checks if the values of two operands are equal or not. If the values are not equal, then the condition becomes true. | (A != B) is true. |
| > | Checks if the value of left operand is greater than the value of right operand. If yes, then the condition becomes true. | (A > B) is not true. |
| < | Checks if the value of left operand is less than the value of right operand. If yes, then the condition becomes true. | (A < B) is true. |
| >= | Checks if the value of left operand is greater than or equal to the value of right operand. If yes, then the condition becomes true. | (A >= B) is not true. |
| <= | Checks if the value of left operand is less than or equal to the value of right operand. If yes, then the condition becomes true. | (A <= B) is true. |
Logical Operators
Following table shows all the logical operators supported by C language. Assume variable A holds 1 and variable B holds 0, then −
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| && | Called Logical AND operator. If both the operands are non-zero, then the condition becomes true. | (A && B) is false. |
| Called Logical OR Operator. If any of the two operands is non-zero, then the condition becomes true. | (A B) is true. | |
| ! | Called Logical NOT Operator. It is used to reverse the logical state of its operand. If a condition is true, then Logical NOT operator will make it false. | !(A && B) is true. |
Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operator works on bits and perform bit-by-bit operation. The truth tables for &, , and ^ is as follows −
| p | q | p & q | p q | p ^ q |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Assume A = 60 and B = 13 in binary format, they will be as follows −
Key generator corel draw x5 free download. A = 0011 1100
B = 0000 1101
-----------------
Dragon ball xenoverse 2 key generator survey. A&B = 0000 1100
A B = 0011 1101
A^B = 0011 0001
~A = 1100 0011
The following table lists the bitwise operators supported by C. Assume variable 'A' holds 60 and variable 'B' holds 13, then −
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| & | Binary AND Operator copies a bit to the result if it exists in both operands. | (A & B) = 12, i.e., 0000 1100 |
| Binary OR Operator copies a bit if it exists in either operand. | (A B) = 61, i.e., 0011 1101 | |
| ^ | Binary XOR Operator copies the bit if it is set in one operand but not both. | (A ^ B) = 49, i.e., 0011 0001 |
| ~ | Binary One's Complement Operator is unary and has the effect of 'flipping' bits. | (~A ) = ~(60), i.e,. -0111101 |
| << | Binary Left Shift Operator. The left operands value is moved left by the number of bits specified by the right operand. | A << 2 = 240 i.e., 1111 0000 |
| >> | Binary Right Shift Operator. The left operands value is moved right by the number of bits specified by the right operand. | A >> 2 = 15 i.e., 0000 1111 |
Assignment Operators
The following table lists the assignment operators supported by the C language −
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Simple assignment operator. Assigns values from right side operands to left side operand | C = A + B will assign the value of A + B to C |
| += | Add AND assignment operator. It adds the right operand to the left operand and assign the result to the left operand. | C += A is equivalent to C = C + A |
| -= | Subtract AND assignment operator. It subtracts the right operand from the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. | C -= A is equivalent to C = C - A |
| *= | Multiply AND assignment operator. It multiplies the right operand with the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. | C *= A is equivalent to C = C * A |
| /= | Divide AND assignment operator. It divides the left operand with the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand. | C /= A is equivalent to C = C / A |
| %= | Modulus AND assignment operator. It takes modulus using two operands and assigns the result to the left operand. | C %= A is equivalent to C = C % A |
| <<= | Left shift AND assignment operator. | C <<= 2 is same as C = C << 2 |
| >>= | Right shift AND assignment operator. | C >>= 2 is same as C = C >> 2 |
| &= | Bitwise AND assignment operator. | C &= 2 is same as C = C & 2 |
| ^= | Bitwise exclusive OR and assignment operator. | C ^= 2 is same as C = C ^ 2 |
| = | Bitwise inclusive OR and assignment operator. | C = 2 is same as C = C 2 |
Misc Operators ↦ sizeof & ternary
Besides the operators discussed above, there are a few other important operators including sizeof and ? : supported by the C Language.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| sizeof() | Returns the size of a variable. | sizeof(a), where a is integer, will return 4. |
| & | Returns the address of a variable. | &a; returns the actual address of the variable. |
| * | Pointer to a variable. | *a; |
| ? : | Conditional Expression. | If Condition is true ? then value X : otherwise value Y |
Operators Precedence in C
C-diff Bacteria Infection
Operator precedence determines the grouping of terms in an expression and decides how an expression is evaluated. Certain operators have higher precedence than others; for example, the multiplication operator has a higher precedence than the addition operator.
For example, x = 7 + 3 * 2; here, x is assigned 13, not 20 because operator * has a higher precedence than +, so it first gets multiplied with 3*2 and then adds into 7.
Here, operators with the highest precedence appear at the top of the table, those with the lowest appear at the bottom. Within an expression, higher precedence operators will be evaluated first.
| Category | Operator | Associativity |
|---|---|---|
| Postfix | () [] -> . ++ - - | Left to right |
| Unary | + - ! ~ ++ - - (type)* & sizeof | Right to left |
| Multiplicative | * / % | Left to right |
| Additive | + - | Left to right |
| Shift | << >> | Left to right |
| Relational | < <= > >= | Left to right |
| Equality | != | Left to right |
| Bitwise AND | & | Left to right |
| Bitwise XOR | ^ | Left to right |
| Bitwise OR | Left to right | |
| Logical AND | && | Left to right |
| Logical OR | Left to right | |
| Conditional | ?: | Right to left |
| Assignment | = += -= *= /= %=>>= <<= &= ^= = | Right to left |
| Comma | , | Left to right |