Bash Ssh Generate Key Login Without Password
Posted By admin On 16.12.20You can login to a remote Linux server without entering password in 3 simple steps using ssky-keygen and ssh-copy-id as explained in this article.
ssh-keygen creates the public and private keys. ssh-copy-id copies the local-host’s public key to the remote-host’s authorized_keys file. ssh-copy-id also assigns proper permission to the remote-host’s home, ~/.ssh, and ~/.ssh/authorized_keys.
This article also explains 3 minor annoyances of using ssh-copy-id and how to use ssh-copy-id along with ssh-agent.
Apr 09, 2015. SSH login without password Your aim. You want to use Linux and OpenSSH to automate your tasks. Therefore you need an automatic login from host A / user a to Host B / user b.
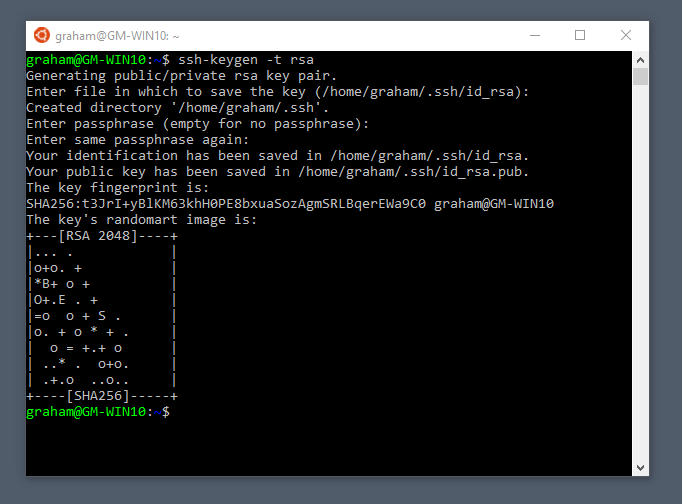
The simplest way to generate a key pair is to run ssh-keygen without arguments. In this case, it will prompt for the file in which to store keys. Here's an example: klar (11:39) ssh-keygen Generating public/private rsa key pair. 3d map generator terrain from heightmap actiavtion key. Feb 19, 2019 Copy the public key. Now that you have generated an SSH key pair, in order to be able to login to your server without a password you need to copy the public key to the server you want to manage. The easiest way to copy your public key to your server is to use a command called ssh-copy-id. If you want to auto-login without a password, here's how to setup SSH to use encryption keys to do so. On the Server. Use ssh to login to your server under the account name you want to use. Run ssh-keygen to create an encryption key pair, the public and private keys. You can just hit return for each question.
Step 1: Create public and private keys using ssh-key-gen on local-host
Step 2: Copy the public key to remote-host using ssh-copy-id
Note: ssh-copy-id appends the keys to the remote-host’s .ssh/authorized_key.
Step 3: Login to remote-host without entering the password
The above 3 simple steps should get the job done in most cases.
We also discussed earlier in detail about performing SSH and SCP from openSSH to openSSH without entering password.
If you are using SSH2, we discussed earlier about performing SSH and SCP without password from SSH2 to SSH2 , from OpenSSH to SSH2 and from SSH2 to OpenSSH.
Using ssh-copy-id along with the ssh-add/ssh-agent

When no value is passed for the option -i and If ~/.ssh/identity.pub is not available, ssh-copy-id will display the following error message.
If you have loaded keys to the ssh-agent using the ssh-add, then ssh-copy-id will get the keys from the ssh-agent to copy to the remote-host. i.e, it copies the keys provided by ssh-add -L command to the remote-host, when you don’t pass option -i to the ssh-copy-id.
Ssh Without Password Key
Three Minor Annoyances of ssh-copy-id
Following are few minor annoyances of the ssh-copy-id.
- Default public key: ssh-copy-id uses ~/.ssh/identity.pub as the default public key file (i.e when no value is passed to option -i). Instead, I wish it uses id_dsa.pub, or id_rsa.pub, or identity.pub as default keys. i.e If any one of them exist, it should copy that to the remote-host. If two or three of them exist, it should copy identity.pub as default.
- The agent has no identities: When the ssh-agent is running and the ssh-add -L returns “The agent has no identities” (i.e no keys are added to the ssh-agent), the ssh-copy-id will still copy the message “The agent has no identities” to the remote-host’s authorized_keys entry.
- Duplicate entry in authorized_keys: I wish ssh-copy-id validates duplicate entry on the remote-host’s authorized_keys. If you execute ssh-copy-id multiple times on the local-host, it will keep appending the same key on the remote-host’s authorized_keys file without checking for duplicates. Even with duplicate entries everything works as expected. But, I would like to have my authorized_keys file clutter free.
If you like this article, please bookmark it on Delicious and Stumble it.
If you enjoyed this article, you might also like.
Next post: The Evolution and Future of Communication Technology
Previous post: How To Manage Dell Servers using OMSA – OpenManage Server Administrator On Linux
Secure Shell (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol used for secure connection between a client and a server and supports various authentication mechanisms. It is also used to transfer files from one computer to another computer over the network using secure copy (SCP) Protocol.
In this article we will show you how to setup password-less login on CentOS 7, RHEL 7, RHEL 8 using ssh keys to connect to remote Linux servers without entering password. Using Password-less login with SSH keys will increase the trust between two Linux servers for easy file synchronization or transfer.
In this example we will setup SSH password-less automatic login from server 192.168.1.5 as user rasho to 192.168.1.8 with user miroslav.
How do I Setup SSH Passwordless Login
To setup a passwordless SSH login in Linux all you need to do is to generate a public authentication key and append it to the remote hosts ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file.
The following command will generate a new 4096 bits SSH key pair with your email address as a comment:
Press Enter to accept the default file location and file name:
Next, the ssh-keygen tool will ask you to type a secure passphrase. Whether you want to use passphrase its up to you, if you choose to use passphrase you will get an extra layer of security. In most cases developers and system administrators are using SSH without a passphrase because they are useful for fully automated processes. If you don’t want to use passphrase just press Enter
The whole interaction looks like this:
Copy the public SSH key to remote host
Copying the key is a simple task and that can be completed by using ssh-copy-id command as shown.
When prompted for the remote user’s password, simply enter it. This will create the .ssh directory if missing and the authorized_keys file with appropriate permissions.
Test SSH Passwordless Login
Now that we have the key copied to our remote server, we can test the connection. You should not be asked for password:
Ssh Generate Key Unix
If everything went well, you will be logged in immediately.
Disabling SSH Password Authentication
To add an extra layer of security to your server you can disable the password authentication for SSH.
Log into your remote server with SSH keys:
Open the SSH configuration file /etc/ssh/sshd_config:
Search for the following directives and modify as it follows:
Once you are done save the file and restart the SSH service.
Conclusion
In this tutorial you learned how to SSH to your CentOS 7, RHEL 7, RHEL 8 system using passwordless ssh key. I hope the process was easy. If you have any questions, please post them in the comment section below.